“IF MAN KNEW HOW TO COMBINE MACHINES WITH CREATIVE SPIRIT, THEY WILL BE THE SERVANT AND LIBERATION OF MANKIND.” F. L. Wright
Imagine a cursor that moves by itself on the screen, selects and compiles fields, clicking independently.
Imagine words typing on your computer with no controls.
It does sound like science fiction, right? It’s actually quite the opposite. It is not an “invisible hand”, but an “automaton” taking control of your mouse and keyboard and uses it, just as you would.
Why is it important?
Below is a historical background on RPA, the transformation revolutionizing the world of business operations.
WHAT IS ROBOTIC AUTOMATION, IN SHORT, RPA?
The robot software that allows this automation is commonly known as Robotic Process Automation or more simply RPA.
Robotic Process automation is defined as the set of technologies, products and processes developed for the automation of working processes. If chatbot technology (we have talked about it here) deals with communicating with customers, the RPA uses “smart” software that can mechanically perform all the repetitive tasks of operators.
The software manages to interact with different computer applications just like a user, taking control of the mouse and keyboard to emulate their behavior.
The RPA is able to move among different applications, select fields, copy and paste information from one part to another, thanks to configuration established rules; it can go through the user interface to find data and use applications such as operators do, automating tasks and processes that replicate alike.
Repetitive processes automation is vital for many businesses because it makes cost reduction effective and can get a higher economic value in terms of use of task resources. To date, the automation of activities, such as workflow, has always been based on structured data sources through internal Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) or ad-hoc scripts for the back-end systems. Since Robotic Process Automation has come along, however, it is also possible to automate activities based on unstructured data, such as images or scanned documents, through the use of elements based on artificial intelligence (AI).
Thanks to AI these software are able to learn routine activities and turn them into robotic operations, adapting to the changes introduced in the environment in which they operate; simply put: they “observe” users performing some work, and create a list of actions that will then be repeated.
GOODBYE REPETITIVE TASKS
The intelligent RPA software is able to automate a number of processes in different sectors. Not all automatable tasks, however, need this technology, so the most suitable are:
- Processes of data acquisition, entry and search;
- Applications start;
- Data transferring through applications.
In simple terms an operator, after receiving a request for a service, launches the RPA that navigates through the various applications and retrieves all data needed to generate an offer; once the customer accepts, the software resumes the work and carries out all the necessary tasks to activate it.
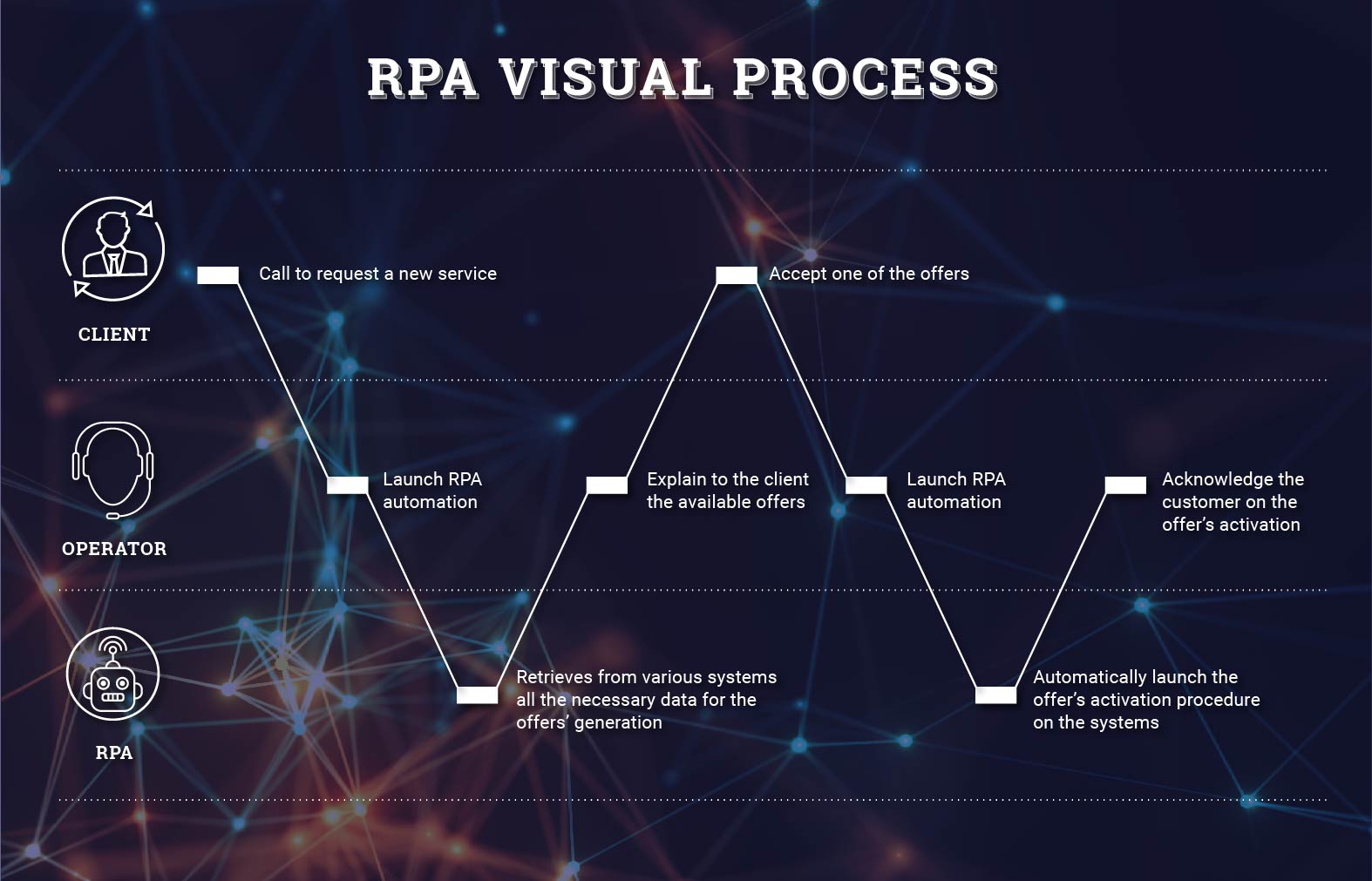
THE POTENTIAL OF ROBOTIC PROCESS AUTOMATION
Robotic Process Automation owes its success above all to the extreme precision and low cost of this technology. Using the RPA in many of the back-office or front-office processes gives companies the opportunity to transform its workflow by optimizing it, so that the human workforce manages more profitable tasks.
Detailing benefits that this robot software brings:
1. Reduction of the margin of error in the execution of the tasks
Once set up, software greatly reduces error probability: thanks to the AI they can learn from mistakes and improve their performance.
2. Processes speed increase
Robots are 15 times faster than humans. In addition, they are able to run long and diversified processes simultaneously, as they require the use of different systems and applications. They can do in a few seconds what an operator would accomplish in three working days.
3. Constant control and check
You can have total control and check constantly processes and errors. It is possible, in fact, at any time, to check and verify the work performed by bots through a tasks log system.
4. Flexibility
Robots can handle a large amount of input, even in the event of sudden increases in the load of requests to be processed. Also, you can use them throughout the year, just like the chatbots.
5. Simple implementation
Implementing RPA is quick and easy. It does not impact on pre-existing computer systems, as bots use the information system exactly like a human user does.
6. Cost reduction
The costs for back-office tasks are reduced through the implementation of automated processes, giving the workforce the ability to deal with higher strategic value operations. Performing tasks more quickly, they can also make more ROI faster.
WHAT IS FUTURE FOR THE RPA?
As we have seen, the RPA is a robot software that automates low economic value and rule-based repetitive tasks.
According to a recent study by McKinsey and Company on digital disruption technologies, it is assumed that technology exploiting automation processes – such as RPA – will be the one with the biggest impact on the market, the second if we consider mobile internet for smartphones and tablets. It is believed that the intelligent software market will reach 6.7 trillion dollars by 2025.
We should hypothesize that Robotic Process Automation is bound to become one of the most important technologies, which can contribute not only to the sectors mentioned above, but in general to all sectors.
This scenario can be achieved by integrating robotic automation with even smarter technologies, such as AI and Machine Learning.
An evolution that implies robots’ learning from actions that push them to a higher level than their initial programming – it is, in fact, proved that these automates are able to learn from unexpected errors in an adaptive way improving their performance over time. So what’s next?



